
- #UBUNTU SUDO NOT AVAILABLE SWITCH TO ROOT HOW TO#
- #UBUNTU SUDO NOT AVAILABLE SWITCH TO ROOT INSTALL#
If you have a sudo package installed as explained in Step 1.1 and still you are getting sudo command not found error. Solution2 - Setup path variable to fix sudo command not found errors Now you will not get any " sudo command not found error" as it's fixed now.

Press Ctrl + X and press " Y" to save the file and exit from the nano editor.Įxit from the root shell and check the sudo command functionality.
#UBUNTU SUDO NOT AVAILABLE SWITCH TO ROOT INSTALL#
Step1.3 Run apt command to install sudo package in Ubuntu/Debian # apt install sudo If you don't have a root password, then follow this link to reset your root password. You would need root access to achieve this. If you don't have the sudo package installed, run the following command to install it in Ubuntu or Debian based distros. Then you can directly move to solution-2 to fix the " sudo: command not found error". If you can find package name sudo with " installed" status as shown in the image. Follow these steps to fix it - Step1.1 List installed packages in Ubuntu and look for the "sudo" package $ apt list -installed | grep -i sudo Still, you may get this situation when you have installed the Debian Linux with the minimal package. This is very uncommon when sudo is not installed by default with Linux installation. Let's deep dive and find the fixes for different scenarios - Solution-1 Check and install sudo package I am running this command in Ubuntu 21.04 installed as VM.
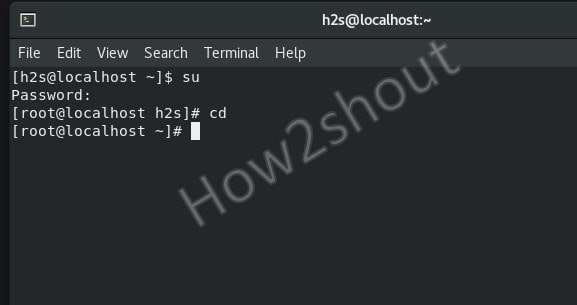

As you will see in the image, running the "sudo ifconfig -a" command results in " bash: /usr/bin/sudo: No such file or directory error".
#UBUNTU SUDO NOT AVAILABLE SWITCH TO ROOT HOW TO#
How to fix sudo command not found error in Debian/Ubuntu like DistrosĪs we discussed already, there may be many reasons to encounter this error. The " sudoers" file controls, who can use the sudo command to gain elevated access and location is /etc/sudoers in all Linux distributions. Also, the operations which are only permitted by a root user can be done using a normal user with sudo rights. It allows running any Linux command with elevated privileges to run administrative tasks. Sudois one of the famous prefixes to any command you run in the Linux world.
Just do ls -l /etc | grep sudoers and see if the output is somthing like this: -r-r- 1 root root 574 20:34 sudoers Apart from that check if the file permission part is correct. First of all if you haven't touched sudo or changed anything on /etc then its just your fear and you should read what Sergey has to say.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
